알고리즘
AVL 트리
AVL은 해당 논문을 발표한 G.M. Adelson-Velskii와 E.M. Landis의 이름을 따서 지은 이름
AVL 트리 정의
- 균형 이진트리
- 완전 이진트리는 검색 시 O(log N) 시간 복잡도를 보장
- AVL 트리는 균형 인수(Balance Factor)을 이용해서, 완전 이진 트리에 가까운 형태를 구현
균형 인수 = 왼쪽 자식 높이 - 오른쪽 자식 높이
=> 균형 인수가 2 이상 차이가 날 떄 문제가 있다고 판단
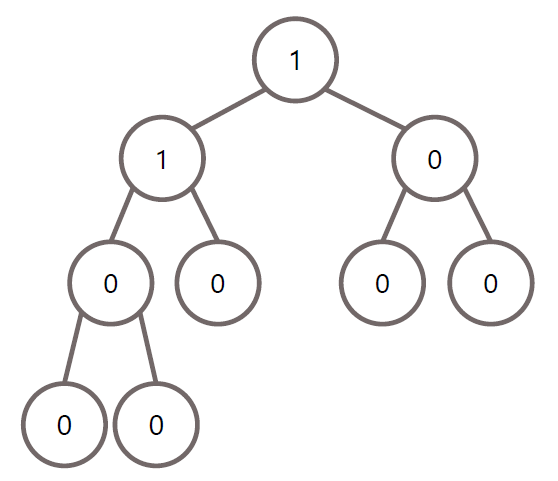
따라서 모든 노드의 균형 인수가 1, 0, -1로 구성
그렇지 않은 경우 회전(Rotation)을 통해 트리 재구성
회전(Rotation)
AVL 트리는 총 4가지 형식에 의해 균형이 깨질 수 있다
| 형식 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| LL | X의 왼쪽 자식의 왼쪽에 삽입하는 경우 |
| LR | X의 왼쪽 자식의 오른쪽에 삽입하는 경우 |
| RR | X의 오른쪽 자식의 오른쪽에 삽입하는 경우 |
| RL | X의 오른쪽 자식의 왼쪽에 삽입하는 경우 |
초기 상태
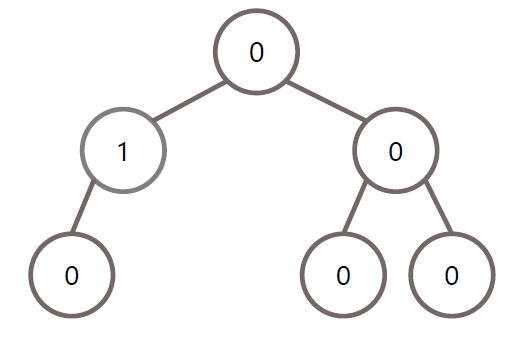
LL 회전 조건
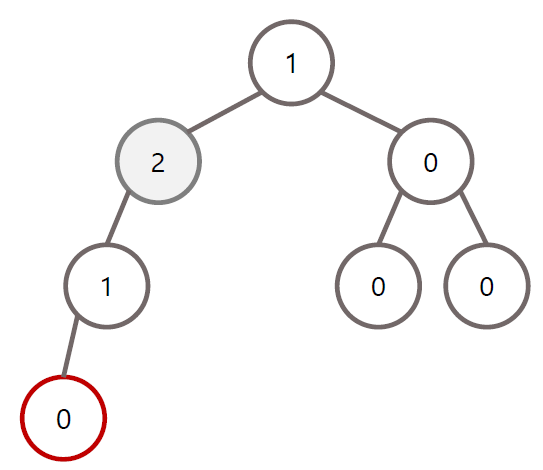
LR 회전 조건
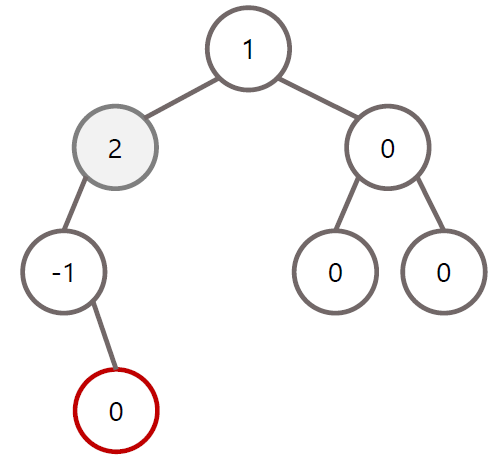
초기 상태
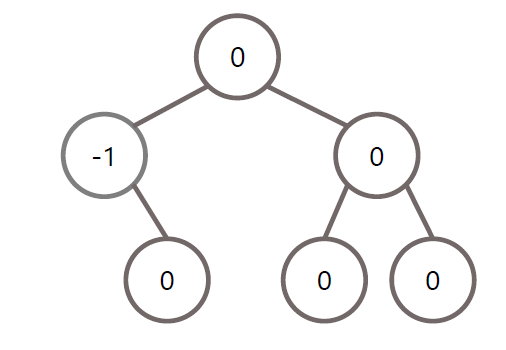
RR 회전 조건
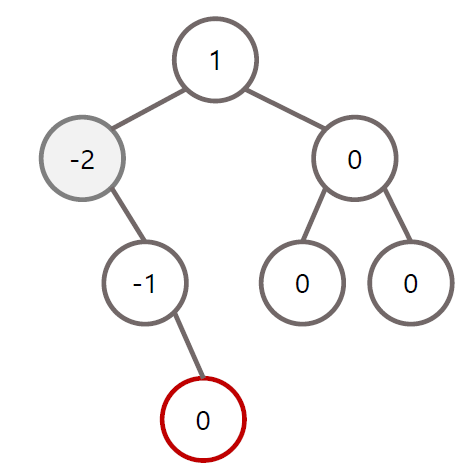
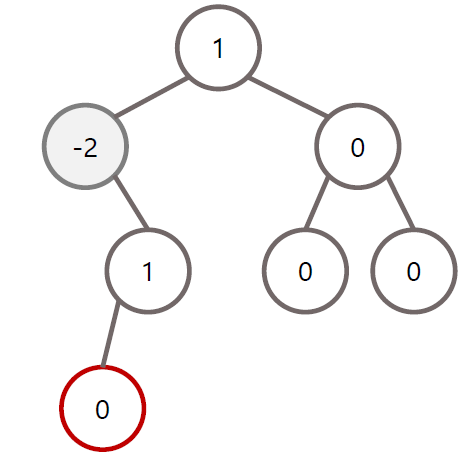
RL 회전 조건
AVL 트리의 LL 회전
노드 X를 기준으로 LL 회전을 수행
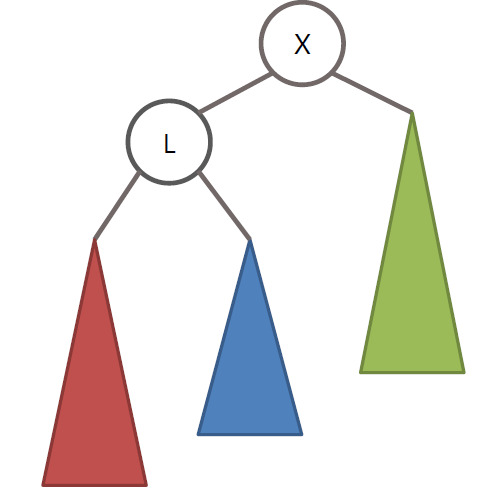
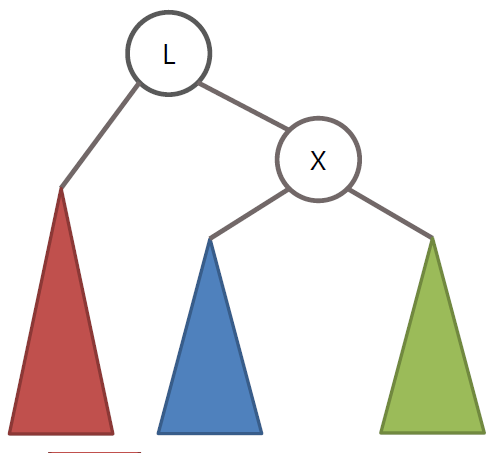
RR 회전은 LL 회전의 정반대
AVL 트리의 LR 회전
왼쪽 노드인 L노드를 기준으로 RR회전을 수행 후 노드 X를 기준으로 LL회전 수행
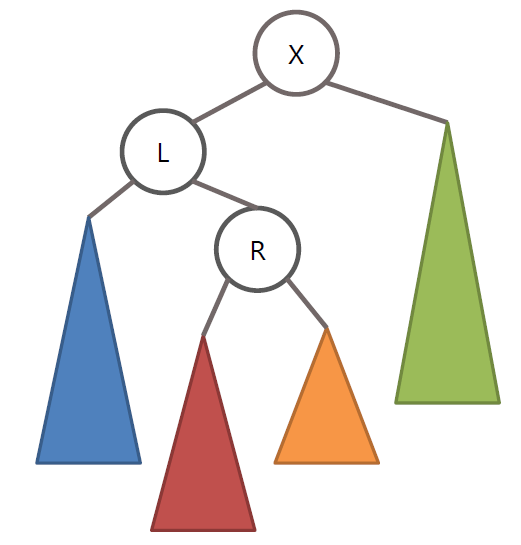
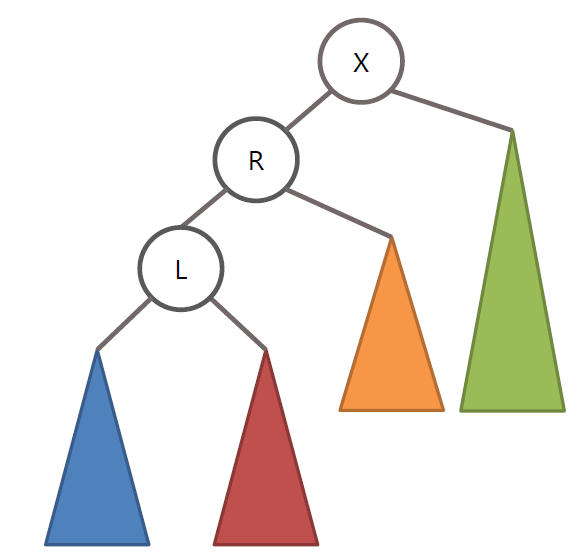
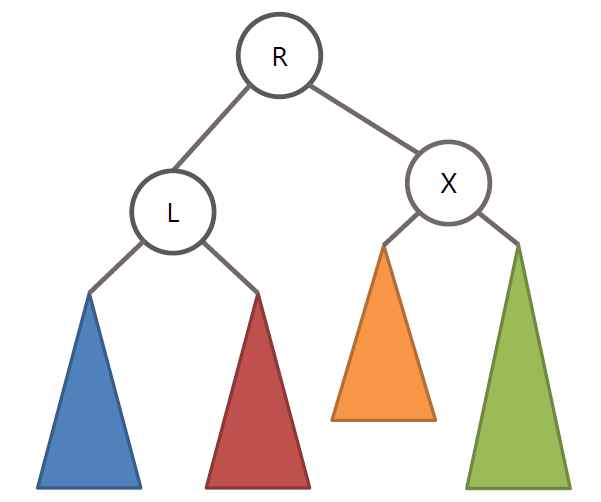
RL 회전 또한 LR 회전의 정 반대
AVL 트리의 균형 잡기
- AVL 트리의 균형 잡기는 각 노드가 삽입 될 때마다 수행
- 삽입 과정에 시간 복잡도는 O(log N)
- 각 트리의 균형 잡기는 삽입 시 모든 노드에 대해 수행되기에 O(1)의 시간 복잡도를 만족해야 함
AVL 트리의 삽입과 출력
삽입 : 일반적인 이진 탐색 트리와 흡사하지만 삽입 시 모든 노드에 대해 균형 잡기를 수행
출력 : 트리의 너비가 높이보다 크기때문에 세로 방향으로 출력
코드 구현(C++)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
} *root;
class AVLtree {
public :
//노드의 높이를 구함
int getHeight(Node*);
//균형인수를 구함
int getDiff(Node*);
//RR회전 함수
Node* rotateRR(Node*);
//LL회전 함수
Node* rotateLL(Node*);
//LR회전 함수
Node* rotateLR(Node*);
//RL회전 함수
Node* rotateRL(Node*);
//트리 균형을 맞추는 함수
Node* balance(Node*);
//새로운 노드 삽입 함수
Node* insertNode(Node*, int);
//AVL 트리 출력 함수
void display(Node*, int);
//중위 순회
void inorder(Node*);
//전위 순회
void preorder(Node*);
//후위 순회
void postorder(Node*);
//생성자
AVLtree() {
root = NULL;
};
};
int AVLtree::getHeight(Node* node) {
int h = 0;
if (node != NULL) {
//재귀로 왼쪽 오른쪽 검색하고, 더 높은 높이를 고름
int left = getHeight(node->left);
int right = getHeight(node->right);
int maxHeight = max(left, right);
h = maxHeight + 1;
}
return h;
}
int AVLtree::getDiff(Node* node) {
//왼쪽 자식과 오른쪽 자식의 높이의 차이를 반환
int left = getHeight(node->left);
int right = getHeight(node->right);
return left - right;
}
Node* AVLtree::rotateRR(Node* node) {
//오른쪽 자식의 왼쪽 자식을 현재 노드의 오른쪽 자식으로
//오른쪽 자식의 왼쪽 자식을 현재 노드로
//최종적으로 오른쪽 자식을 반환함으로 오른쪽 자식을 현재 노드로 만듬
Node* temp;
temp = node->right;
node->right = temp->left;
temp->left = node;
return temp;
}
Node* AVLtree::rotateLL(Node* node) {
//RR과 반대 방향으로
Node* temp;
temp = node->left;
node->left = temp->right;
temp->right = node;
return temp;
}
Node* AVLtree::rotateLR(Node* node) {
//현재 노드의 왼쪽 자식을 RR, 본인을 LL 회전
Node* temp;
temp = node->left;
node->left = rotateRR(temp);
return rotateLL(node);
}
Node* AVLtree::rotateRL(Node* node) {
//LR과 반대
Node* temp;
temp = node->right;
node->right = rotateLL(temp);
return rotateRR(node);
}
Node* AVLtree::balance(Node* node) {
int factor = getDiff(node);
//왼쪽 서브트리쪽으로 삽입되어 균형이 깨진경우
if (factor > 1) {
//그 왼쪽 자식이 문제일떄
if (getDiff(node->left) > 0) {
node = rotateLL(node);
}
//그 오른쪽 자식이 문제일때
else {
node = rotateLR(node);
}
}
//오른쪽 삽입되어 균형이 깨진경우
else if (factor < -1) {
if (getDiff(node->right) > 0) {
node = rotateRL(node);
}
else {
node = rotateRR(node);
}
}
return node;
}
Node* AVLtree::insertNode(Node* root, int value) {
//트리가 비었을때
if (root == NULL) {
root = new Node;
root->data = value;
root->left = NULL;
root->right = NULL;
return root;
}
else if (value < root->data) {
root->left = insertNode(root->left, value);
root = balance(root);
}
//크기가 같으면 오른쪽에 삽입
else if (value >= root->data) {
root->right = insertNode(root->right, value);
root = balance(root);
}
return root;
}
void AVLtree::display(Node* node, int level) {
//현재 트리가 비어있지않으면
if (node != NULL) {
display(node->right, level + 1);
cout << endl;
//루트라면
if (node == root) {
cout << "Root ->";
}
//현재 레벨보다 낮고 루트가 아닐때
for (int i = 0; i < level && node != root; i++) {
cout << " ";
}
cout << node->data;
display(node->left, level + 1);
}
}
void AVLtree::inorder(Node* node) {
if (node == NULL)
return;
inorder(node->left);
cout << node->data << " ";
inorder(node->right);
}
void AVLtree::preorder(Node* node) {
if (node == NULL)
return;
cout << node->data << " ";
inorder(node->left);
inorder(node->right);
}
void AVLtree::postorder(Node* node) {
if (node == NULL)
return;
inorder(node->left);
inorder(node->right);
cout << node->data << " ";
}
int main(void) {
int choice, item;
AVLtree AVL;
while (1)
{
cout << "\n----------------------------" << endl;
cout << " C++로 구현한 AVL 트리" << endl;
cout << "----------------------------" << endl;
cout << "1. 원소를 삽입할래요." << endl;
cout << "2. AVL 트리를 보여주세요." << endl;
cout << "3. 중위 순회를 하고싶어요." << endl;
cout << "4. 전위 순회를 하고싶어요." << endl;
cout << "5. 후위 순회를 하고싶어요." << endl;
cout << "6. 프로그램을 종료할래요." << endl;
cout << "당신의 선택을 입력하세요 : ";
cin >> choice;
switch (choice)
{
case 1:
cout << "삽입할 정수를 입력하세요 : ";
cin >> item;
root = AVL.insertNode(root, item);
case 2:
if (root == NULL)
{
cout << "현재 트리가 비었습니다." << endl;
continue;
}
cout << "[ AVL 트리 출력 ]" << endl;
AVL.display(root, 1);
break;
case 3:
cout << "[ 중위 순회 ]" << endl;
AVL.inorder(root);
cout << endl;
break;
case 4:
cout << "[ 전위 순회 ]" << endl;
AVL.preorder(root);
cout << endl;
break;
case 5:
cout << "[ 후위 순회 ]" << endl;
AVL.postorder(root);
cout << endl;
break;
case 6:
exit(1);
break;
default:
cout << "잘못된 입력입니다." << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
문제점
균형 유지로 인해 일정 수준의 검색 성능을 보장하는 대신 자료의 개수가 증가하여 트리의 높이가 계속해서 높아진다는 문제점이 있습니다.
그리고 자료의 추가나 삭제가 빈번하게 발생하면 균형 유지에 소모되는 시간이 많다는 문제점이 있습니다.